Describing Results
This webpage provides information on how to describe the results from a questionnaire. It provides language for describing quantities, group sizes, specific features and reporting verbs. It includes model answers and a range of practice activities (bar charts, pies charts and tables).
Pay-per-Download
Describing Results (questionnaire data) [new 2023]
This lesson teaches students how to describe the results from a questionnaire. It provides language for describing quantities, group sizes, specific features and reporting verbs. It includes model answers and a range of practice activities. Example Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Describing Results Video
A short video on the describing results lesson
Video Worksheet – click here
Describing Results Example
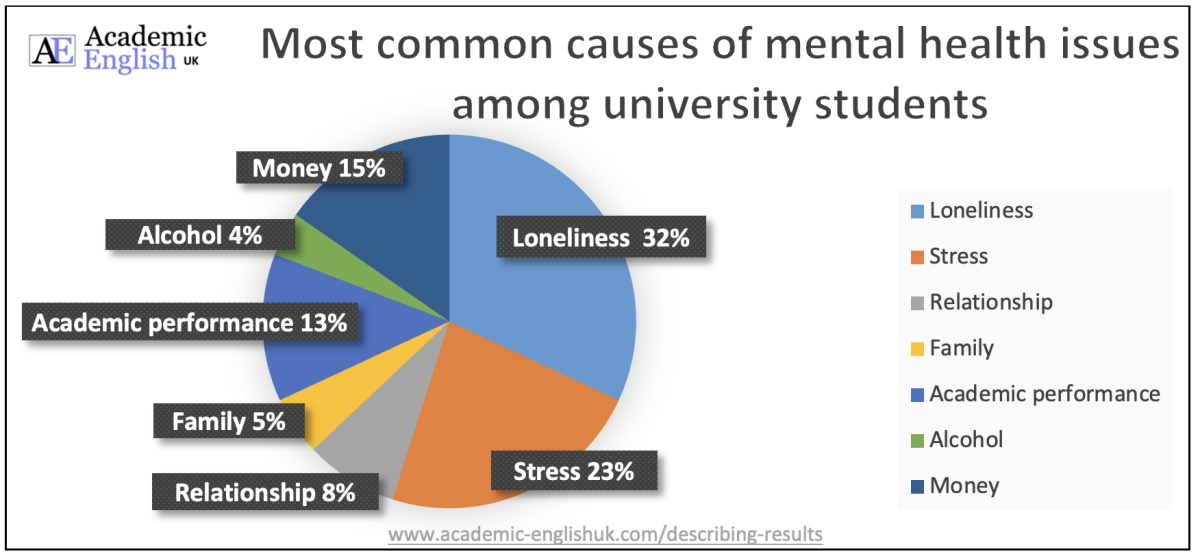
This pie chart has been created from a questionnaire which asked 500 students what the main causes of their mental health issues at university were.
Exercise
Read through these short descriptions of the above data and highlight the reporting verbs and linking words.Then highlight the phrases for describing quantity and adjective collocations. You may need to study the describing results language development below first. Download descriptions here.
- Descriptions
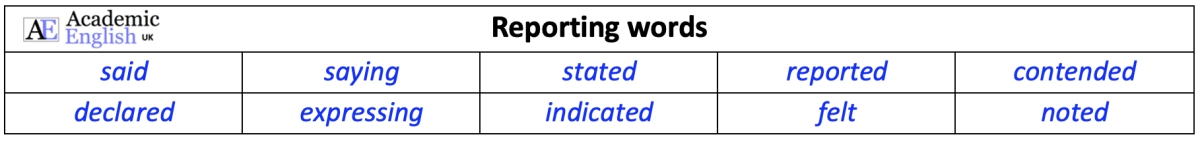
- Reporting verbs & linking words ANSWERS
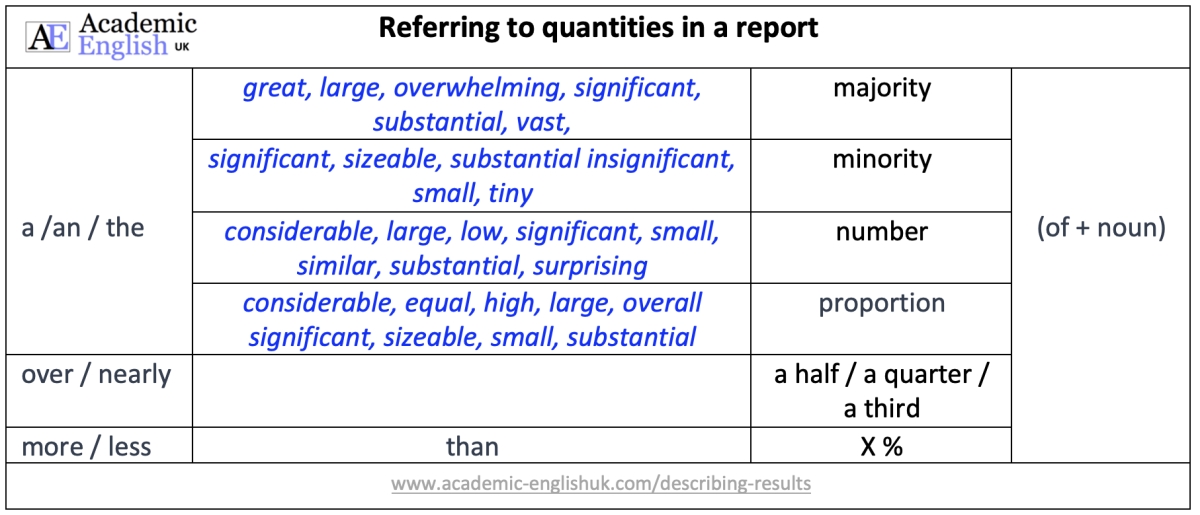
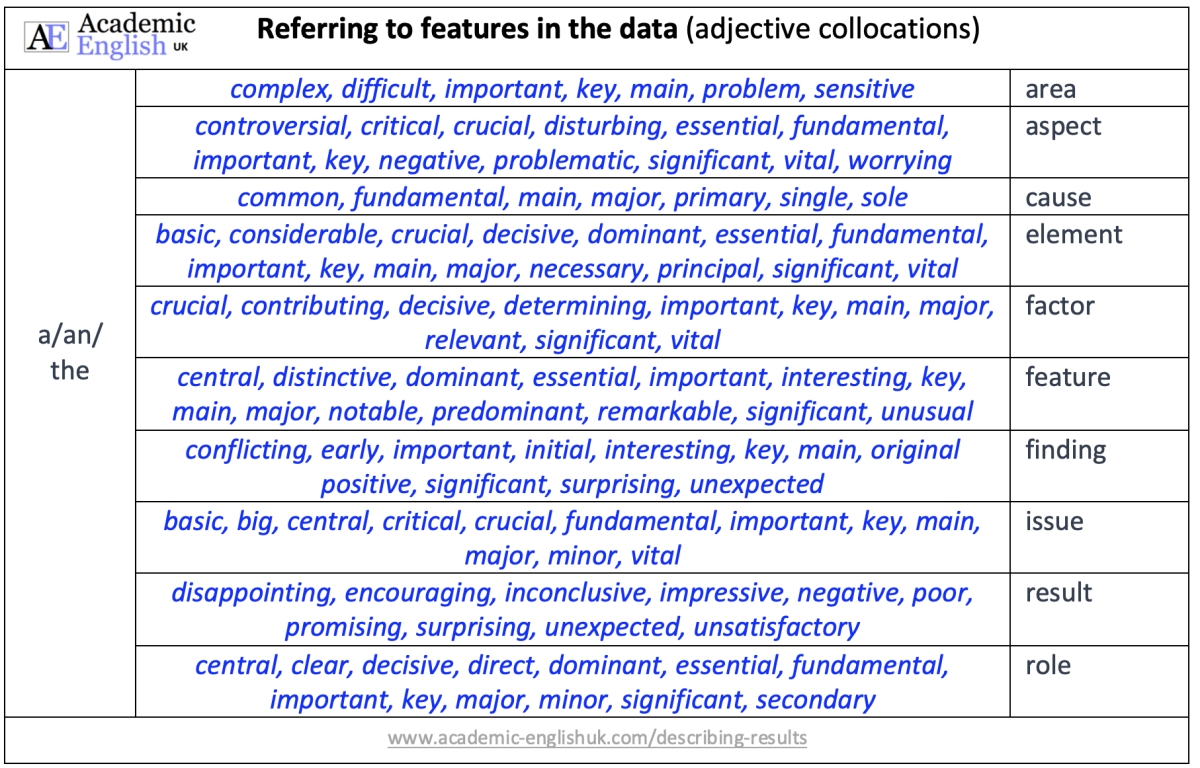
- Describing quantity and adjective collocations ANSWERS
- The most significant finding from the questionnaire is that approximately a third of respondents (32%) said that loneliness was the main cause of their mental health issue at university. This was in contrast to a small number of students (4%) saying that alcohol was the primary cause.
- Although the majority of students stated that loneliness and stress were the most significant mental health issues at university at 55%, academic performance and money problems were also reported to be fundamental at 28%.
- A small minority of students (4%) contended that their mental health issues were attributed to alcohol abuse, whereas a similar number (5%) declared family issues were the main contributing factor.
- The most significant finding from the questionnaire is that approximately a third of respondents (32%) said that loneliness was the main cause of their mental health issue at university. This was in contrast to a small number of students (4%) saying that alcohol was the primary cause.
- Although the majority of students stated that loneliness and stress were the most significant mental health issues at university at 55%, academic performance and money problems were also reported to be fundamental at 28%.
- A small minority of students (4%) contended that their mental health issues were attributed to alcohol abuse, whereas a similar number (5%) declared family issues were the main contributing factor.
- The most significant finding from the questionnaire is that approximately a third of respondents (32%) said that loneliness was the main cause of their mental health issue at university. This was in contrast to a small number of students (4%) saying that alcohol was the primary cause.
- Although the majority of students stated that loneliness and stress were the most significant mental health issues at university at 55%, academic performance and money problems were also reported to be fundamental (issue) at 28%.
- A small minority of students (4%) contended that their mental health issues were attributed to alcohol abuse, whereas a similar number (5%) declared family issues were the main contributing factor.
Describing Results Language Development
Pay-per-Download
 Describing Results (questionnaire data) [new 2023]
Describing Results (questionnaire data) [new 2023]
This lesson teaches students how to describe the results from a questionnaire. It provides language for describing quantities, group sizes, specific features and reporting verbs. It includes model answers and a range of practice activities. Example Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Other graphical data lessons
Describing graphs – the basics [updated 2023]
This lesson begins by labelling the key features of a graph and naming different graph / chart types. It then provides practice in describing a range of different lines (peak, plummet, etc..). This is followed by a fun activity where in pairs students describe and plot the lines on four graphs. Example. Level: ***** [B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Describing graphs: analysis and evaluation (updated 2023)
This lesson begins with describing basic graphs and suggesting what they could represent. It then provides the language necessary for describing, analysing and evaluating. This is followed by students researching and analysing graphs/charts/tables from the Office of National Statistics (ONS) and giving a short presentation on their findings. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Academic description, analysis & evaluation
This lesson helps to improve students’ awareness and understanding of the difference between description, analysis and evaluation. It includes paragraph analysis, a detailed language review reference sheet and graph and sentence level quotation analysis. – see worksheet example. Time: 120mins. Level ***** [[B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP