Critical Thinking Skills
What is critical thinking?
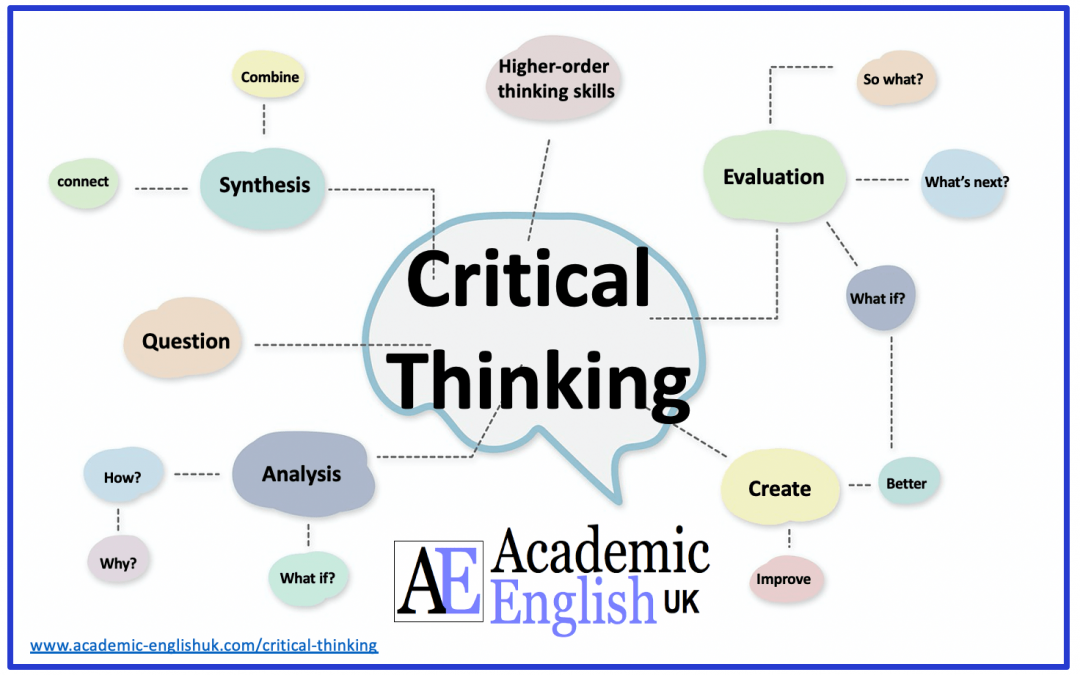
Critical thinking is derived from the ancient Greek word Kritikos meaning questioning. Universal scholarly agreement is based on the understanding that it is the higher order cognitive skills of analysing, evaluating and creating to determine merit, affirm true worth and assess validity in any discourse. Criticality is an essential tool of inquiry and reflects the ability of taking responsibility of one’s mind through initiating self-reflective discussion of always asking for clarification, questioning beliefs or theories and drawing open-minded conclusions (Wilson, 2018; Academic English UK)
Critical Thinking Worksheets / Lessons
Critical Analysis Reading Texts (new for 2024)
Critical thinking definitions from universities
‘Critical thinking is a systematic evaluation of the arguments, ideas and theories of others. The basic premise of critical thinking involves asking critical questions to form an educated opinion of whether or not those resources are credible’ (Stanford University, 2018).
‘Critical thinking consists of three elements: a capacity to spot weakness in other arguments, a passion for good evidence, and a capacity to reflect on your own views and values with an eye to possibly change them’ (Harvard University, 2018).
‘Critical thinking is the art of making clear, reasoned judgements based on interpreting, understanding, applying and synthesising evidence gathered from observation, reading and experimentation’ (The University of Edinburgh, 2020).
‘To think critically is to examine ideas, evaluate them against what you already know and make decisions about their merit. The aim of critical thinking is to try to maintain an ‘objective’ position. When you think critically, you weigh up all sides of an argument and evaluate its strengths and weaknesses’ (The Open University, 2008).
‘Thinking critically means asking questions. Instead of accepting ‘at face value’ what you read or hear, critical thinkers look for evidence and for good reasons before believing something to be true. This is at the heart of what it means to be a scientist, researcher, scholar or professional in any field. Whatever you are studying, critical thinking is the key to learning and to making progress’ (Plymouth University, 2010).
‘Critical thinking is a key skill that should be applied to all aspects of your studies. As a university student, you need to be able to think critically about the resources and information you use in your work. You need to ask the right questions when reading the work of others; your writing needs to show you have the ability to weigh up different arguments and perspectives and use evidence to help you form your own opinions, arguments, theories and ideas. Critical thinking is about questioning and learning with an open mind’ (Leeds University, 2017).
Pay-per-Download
Terms & Conditions of Use
Dictogloss – a critical thinking definition
 Dictogloss: Critical Thinking
Dictogloss: Critical Thinking
The basic history of critical thinking, the main words associated with it and its importance.Key Language: Verb + noun collocations / critical thinking terminology. Level: ***** [C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Academic Listening Test by AEUK
 Critical Thinking: an introduction – Lecture Listening Lesson
Critical Thinking: an introduction – Lecture Listening Lesson
This lecture focuses on critical thinking at university. It includes a definition, alternative thinking styles, Bloom’s taxonomy and how to apply analysing and evaluation questions to reading and writing. It includes a video, test questions, tapescript and PPT (example). Level ***** [B2/C1] / PPT link in download / Video [10.00] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Speaking: critical thinking discussion: ‘fact over opinion’.
Critical Speaking – 8 questions most people get wrong!
A great lesson for highlighting facts over opinions. This lesson asks students to discuss 8 questions based around a variety of topics. The lesson is based on research by Hans Rosling a UN advisor, professor of international health and medical physician, who argues many people have an over-dramatic world view that its not based on facts. The lesson includes factual data from the World Bank and UN to support all answers. Example. Level: ***** [C1 – High level] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Critical Thinking PDF Lesson Book
Critical Thinking Lesson PDF Book
AMAZING VALUE – Five lessons in one book. Introduction, definition, text analysis reading, lecture listening test, and speaking discussion. Example. TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Listening on the theory of higher thinking skills.
Bloom’s Taxonomy – higher-order thinking skills (new for 2020) – LSU Centre for Academic Success
This short video provides a brief overview of Bloom’s taxonomy: classification of learning levels. It discusses each level but pays particular attention to the higher levels of analysing, evaluating and creating. It is a nice introduction to the theory of critical thinking. Example. Level: ***** [B2/C1] / Video [3.51] / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Bloom’s Cue Cards
Critical Thinking: Bloom’s taxonomy cue questions
This information sheet provides a set of cue questions for each level of the taxonomy. A very helpful resource to accompany the theory of Bloom’s classification of thinking levels. TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
TED Talks 5 Tips for Critical Thinking
5 tips to improve critical thinking – Samantha Agoos
TED TALK: This lecture discusses briefly what is critical thinking and five key strategies to apply to improve critical thinking. It is a good listening as an introduction to criticality. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] / Video [4:16] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
TED Talks Ethical Dilemmas
Would you sacrifice one person to save five?– Eleanor Nelson
TED TALK: This lecture discusses an ethical dilemma called ‘The Trolley Problem’ devised by Philippa Foot (1967). It highlights why this type of ethical analysis is important in contemporary society. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] / Video [4:35] / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Critical Analysis Reading Texts
A short video on how to read a text critically.
Video Worksheet: click here
Text Analysis 1: Going to university
Text Analysis 1: Going to university (updated 2024)
A great lesson for developing and practising critical thinking reading skills. It is a 400-word text on ‘going to university’ with over 15 possible problems. Students use the higher level thinking skills of analysis and evaluation to examine, question and critique the text. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Text Analysis 2: Cost-of-living crisis
Text Analysis 2: Cost-of-living crisis (new 2024)
A great lesson for developing and practising critical thinking reading skills. It is a 400-word text on ‘the cost-of-living crisis’ with over 18 possible problems. Students use the higher level thinking skills of analysis and evaluation to examine, question and critique the text. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Text Analysis 3: Population growth
Text Analysis 3: Population Growth (new 2024)
A great lesson for developing and practising critical thinking reading skills. It is a 400-word text on ‘population growth’ with over 15 possible problems. Students use the higher level thinking skills of analysis and evaluation to examine, question and critique the text. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Coming Soon…
*
Text Analysis 4: Climate Change
Text Analysis 4: Climate Change (new 2024)
A great lesson for developing and practising critical thinking reading skills. It is a 400-word text on ‘climate change’ with over 15 possible problems. Students use the higher level thinking skills of analysis and evaluation to examine, question and critique the text. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Coming Soon…
*
Text Analysis 5: Data Centres
Text Analysis 5: Data Centres (new 2024)
A great lesson for developing and practising critical thinking reading skills. It is a 400-word text on ‘data centres’ with over 15 possible problems. Students use the higher level thinking skills of analysis and evaluation to examine, question and critique the text. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Coming Soon…
*
Questioning worksheets
Critical Thinking Reading & Listening Questions
Critical Thinking: questions to support critical reading
This information sheet provides a range of questions that should be applied when reading any academic text. The answers to these question should be then applied in writing. TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
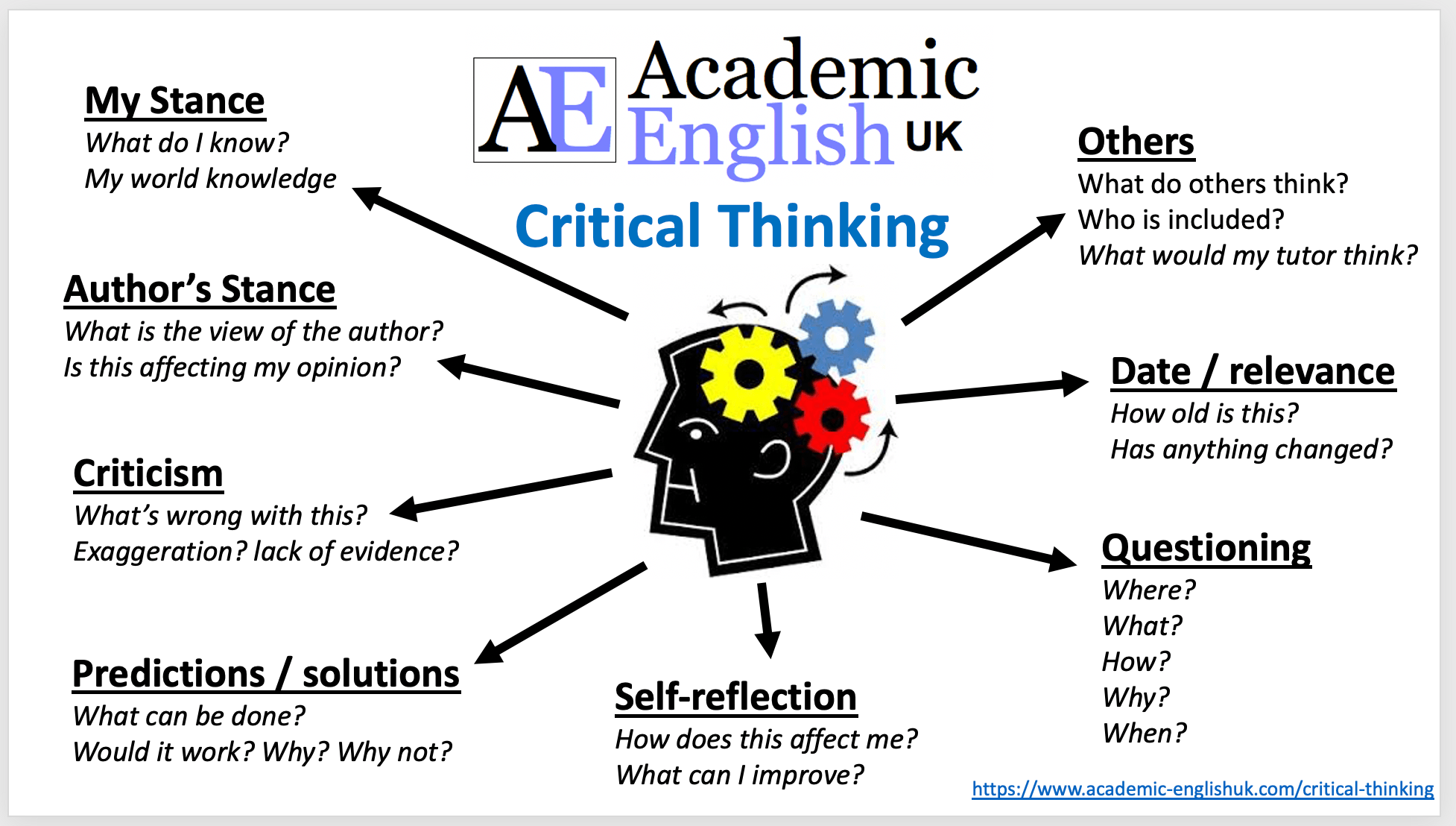
Critical Thinking Infographic
Critical Thinking: cheat sheet infographic
This is a simple infographic offering questions that work to develop critical thinking on any given topic. Whenever your students discover or talk about new information, encourage them to use these questions for sparking debate and the sharing of opinions and insights among each other.TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Critical Thinking Linear Questions
Critical Thinking: a linear question sheet
This information sheet shows the development of an argument: from description to analysis and evaluation. It sets out a linear model of guiding questions that lead into each level of thinking (Plymouth University).TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Critical Thinking Socratic Questions
Critical Thinking: Socratic questioning
This information sheet uses a range of socratic question under the topics of: clarifying, challenging, using evidence, exploring evidence, considering consequences and questioning the question (TES).TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
AEUK Critical Thinking Perspectives
Barriers to critical thinking
Critical Thinking: student barriers to being critical
This information sheet discusses seven key reasons why students struggle to apply critical thinking. From misunderstanding what is critical thinking to lacking confidence in critiquing experts. TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP