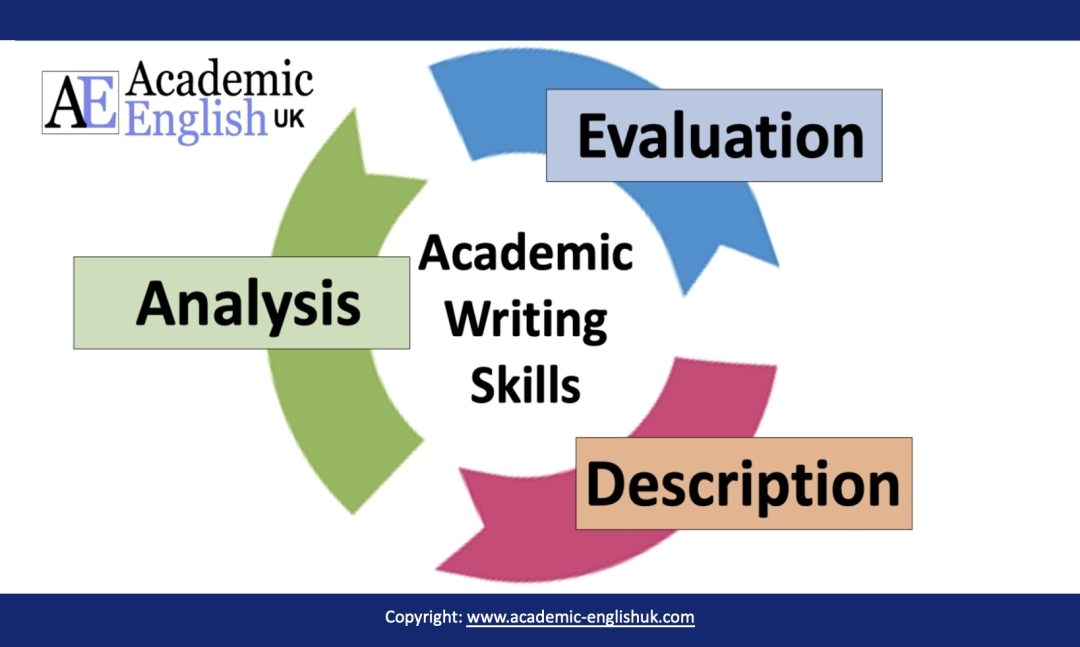
Description, analysis & evaluation
A basic definition of all three terms:
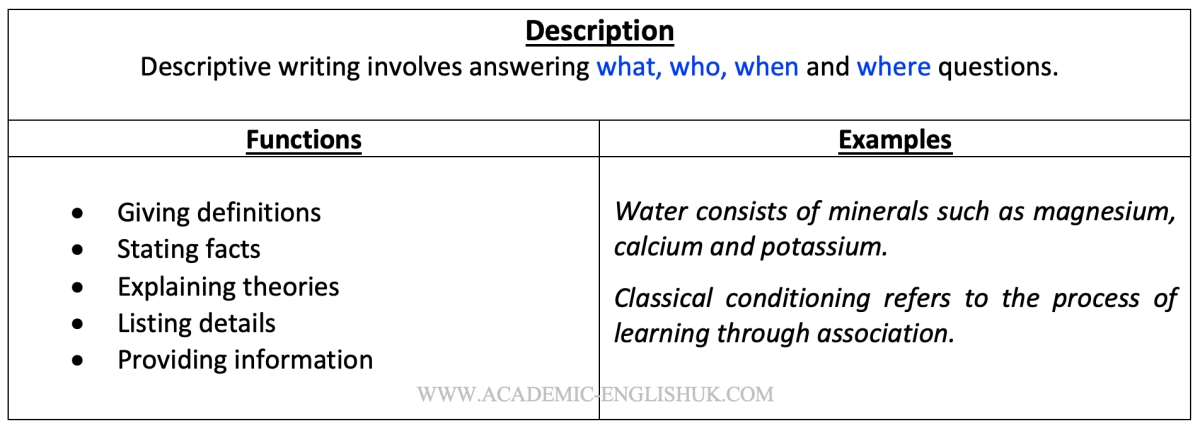
Description: To give a clear and detailed picture of something.
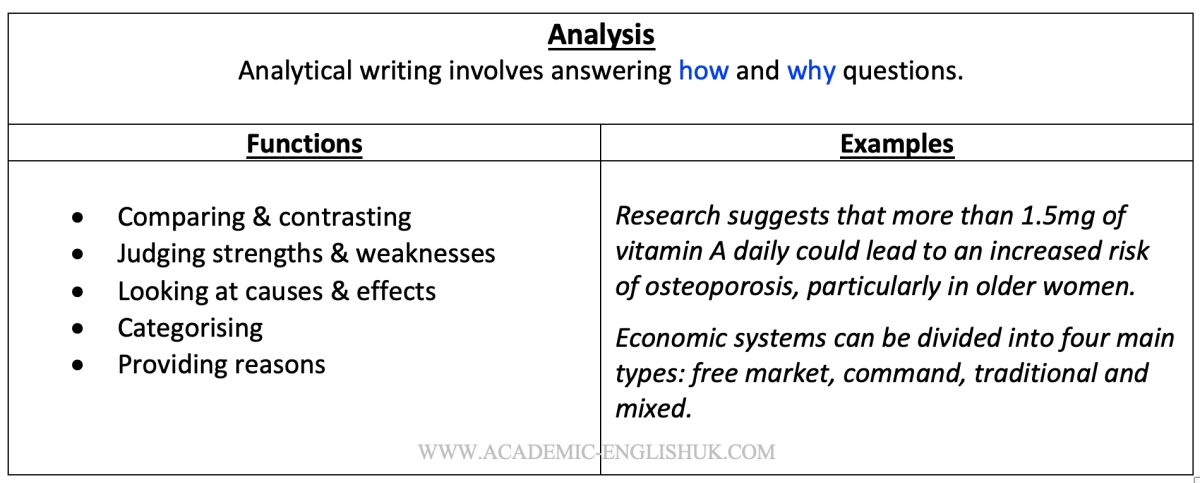
Analysis: To make a methodical and detailed examination.
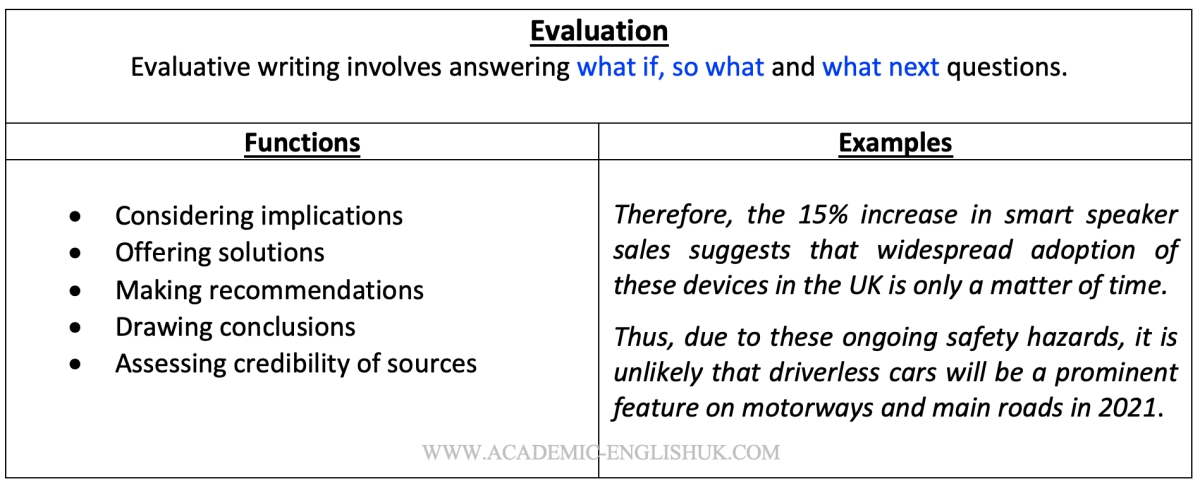
Evaluation: To make judgements about the value of information.
Why is it important?
Academic description, analysis and evaluation video
If you can’t access this YouTube video in your country, go here
Video Worksheet: click here
PDF Lesson Download
Academic description, analysis & evaluation
This lesson helps to improve students’ awareness and understanding of the difference between description, analysis and evaluation. It includes paragraph analysis, a detailed language review reference sheet and graph and sentence level quotation analysis. – see worksheet example. Time: 120mins. Level ***** [[B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Practice Exercises
Exercise 1: Sentence analysis
2. Bioengineering is the application of engineering knowledge to the fields of medicine and biology for the enhancement of human health. [ ]
3. The main issue with carbon capture and storage under the ocean is that CO2 reacts with water and causes the oceans to become too acidic for marine life. [ ]
2.Bioengineering is the application of engineering knowledge to the fields of medicine and biology for the enhancement of human health. [D] Description
3.The main issue with carbon capture and storage under the ocean is that CO2 reacts with water and causes the oceans to become too acidic for marine life. [A] Analysis
Exercise 2: Paragraph analysis
Look at this paragraph and highlight the sections of: description, analysis, evaluation.
Smart home technology
Smart home technology can take many forms, from controlling the lighting and temperature of a room to monitoring the contents of a fridge. As most current smart homes rely on retro-fitting, which is the process of adding home automation features to an existing property and can lead to considerable costs for the homeowner, newer homes are being built with the additional sensors and systems already installed. However, as the amount of smart home devices and applications continues to grow rapidly, it has given rise to compatibility and connectivity issues. As a result, the focus should now shift to standardising the technology’s protocols.
Smart home technology
*Description * Analysis *Evaluation
Smart home technology can take many forms, from controlling the lighting and temperature of a room to monitoring the contents of a fridge. As most current smart homes rely on retro-fitting, which is the process of adding home automation features to an existing property and can lead to considerable costs for the homeowner, newer homes are being built with the additional sensors and systems already installed. However, as the amount of smart home devices and applications continues to grow rapidly, it has given rise to compatibility and connectivity issues. As a result, designers must now focus on standardising the technology’s protocols.
Exercise 3: Graphs, charts and tables
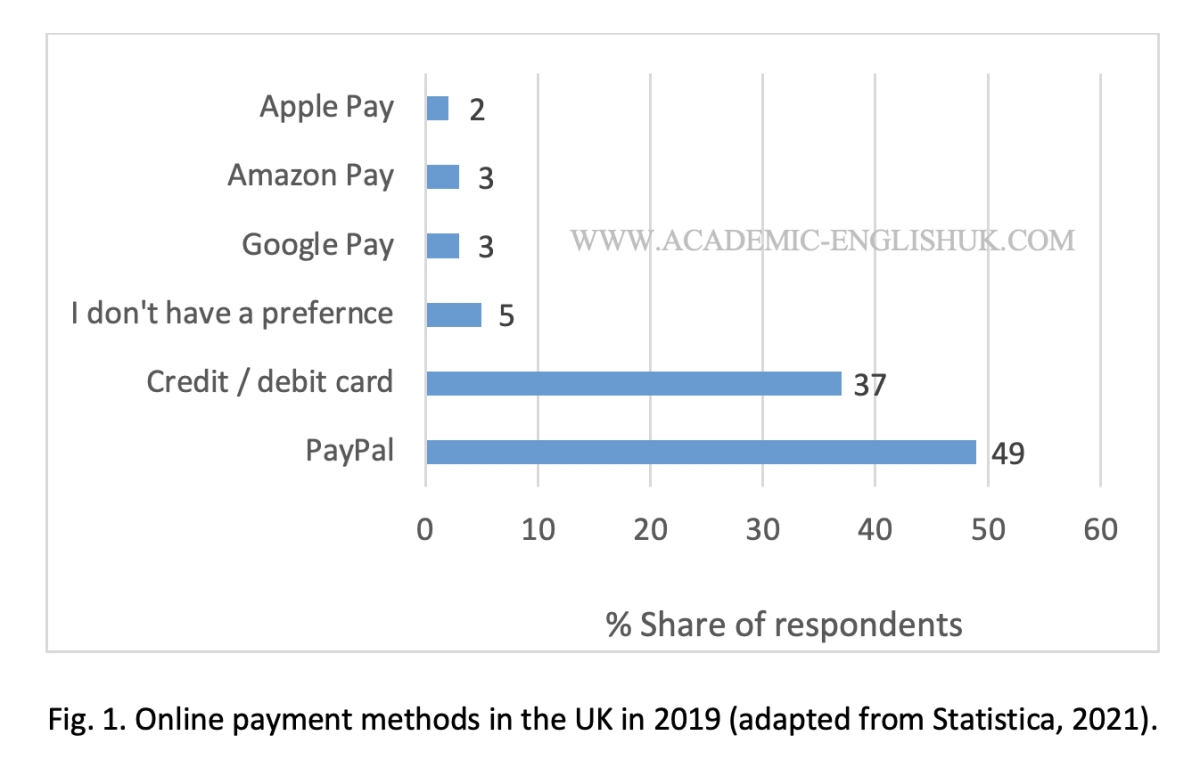
Look at the bar chart and answer the questions for description, analysis.and evaluation.
Description
1, What does the graph show?
2, Which country is the chart referring to?
3. Which year was the data collected?
Description
1, What does the graph show?
- The methods of paying online.
2, Which country is the chart referring to?
- UK
3. Which year was the data collected?
- 2019.
Analysis
1.Which findings are the most significant?
2.How do the findings compare?
3.What is the reason for the trends?
Analysis
1.Which findings are the most significant?
PayPal & credit/debit cards.
2.How do the findings compare?
PayPal at 49%, cards at 37%, Google, Apple, Amazon at 8%.
3.What is the reason for the trends?
PayPal offers security and convenience and has been around for over twenty years so it has built up its brand image. Google, Apple & Amazon are still relatively new and it’s mainly millennials who have embraced these ways of paying.
Evaluation
1. Will the findings change in the future?
2. How will the findings change in the future?
3. What’s your rationale for the changes you mentioned?
Evaluation
1. Will the findings change in the future?
YES, definitely
2. How will the findings change in the future?
Google, Amazon and Apple pay will take more of the market share as their systems become more well-known and secure. PayPal could lose some of its market share as other payment systems enter the market and offer better rates.
3. What’s your rationale for the changes you mentioned?
Mobile payments have increased a great deal in some parts of Asia and credit/debit cards are hardly used in these countries in the current climate so this is a trend that is likely to be seen in the UK over the next few years.
Exercise 4: Quotations
Analyse and evaluate these quotes:
- Analyse and evaluate the quote by David Attenborough (2021) for the UN COP 26 summit.
Quote: “The problems that await the world in the next five to ten years because of climate change are greater than the coronavirus pandemic”.
What the broadcaster and natural historian means in his quote is that as all nations have witnessed the devasting impact of the coronavirus pandemic, and the warning that climate change will have a far more catastrophic effect on the planet, it is now time for countries to come together to question the current economic models and set new targets for reducing global emissions (analysis). This is vital so that the biodiversity of the planet can be protected (evaluation).
- Analyse and evaluate the quote by M. Kit Delgado (2021), Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine and Epidemiology at University of Pennsylvania.
Quote: “Given how beneficial these Smartphone breathalyser devices could be to public health, our findings suggest that oversight or regulation would be valuable”.
The professor argues that current breath alcohol testing devices on smartphones are not fit for purpose, which could have potentially catastrophic consequences (analysis). As technology continues to evolve at such as rapid rate, it is hoped that new standards of mobile breathalysers can be easily reached (evaluation).
Academic description, analysis & evaluation download
Academic description, analysis & evaluation
This lesson helps to improve students’ awareness and understanding of the difference between description, analysis and evaluation. It includes paragraph analysis, a detailed language review reference sheet and graph and sentence level quotation analysis. – see worksheet example. Time: 120mins. Level ***** [[B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Graph and Chart Lessons
Describing Graphs – The Basics [updated 2023]
This lesson begins by labelling the key features of a graph and naming different graph / chart types. It then provides practice in describing a range of different lines (peak, plummet, etc..). This is followed by a fun activity where in pairs students describe and plot the lines on four graphs. Example. Level: ***** [B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Describing graphs: analysis and evaluation (updated 2023)
This lesson begins with describing basic graphs and suggesting what they could represent. It then provides the language necessary for describing, analysing and evaluating. This is followed by students researching and analysing graphs/charts/tables from the Office of National Statistics (ONS) and giving a short presentation on their findings. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Academic description, analysis & evaluation
This lesson helps to improve students’ awareness and understanding of the difference between description, analysis and evaluation. It includes paragraph analysis, a detailed language review reference sheet and graph and sentence level quotation analysis. – see worksheet example. Time: 120mins. Level ***** [[B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
 Describing Results (questionnaire data) [new 2023]
Describing Results (questionnaire data) [new 2023]
This lesson teaches students how to describe the results from a questionnaire. It provides language for describing quantities, group sizes, specific features and reporting verbs. It includes model answers and a range of practice activities. Example Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Critical Thinking Lessons
Dictogloss: Critical thinking
The basic history of critical thinking, the main words associated with it and its importance.Key Language: Verb + noun collocations / critical thinking terminology. Level: ***** [C1] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
 Critical thinking: an introduction – Lecture Listening Lesson
Critical thinking: an introduction – Lecture Listening Lesson
This lecture focuses on critical thinking at university. It includes a definition, alternative thinking styles, Bloom’s taxonomy and how to apply analysing and evaluation questions to reading and writing. It includes a video, test questions, tapescript and PPT (example). Level ***** [B2/C1] / PPT link in download / Video [10.00] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
*
Critical thinking: reading text analysis
A great lesson for developing and practising critical thinking skills. It is a 400-word text on ‘going to university’ with over 15 possible problems. Students use the higher level thinking skills of analysis and evaluation to examine, question and critique the text. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1]
TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Critical speaking: 8 questions most people get wrong!
A great lesson for highlighting facts over opinions. This lesson asks students to discuss 8 questions based around a variety of topics. The lesson is based on research by Hans Rosling a UN advisor, professor of international health and medical physician, who argues many people have an over-dramatic world view that its not based on facts. The lesson includes factual data from the World Bank and UN to support all answers. Example. Level: ***** [C1 – High level] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Critical Thinking Lesson PDF Book
AMAZING VALUE – Five lessons in one book. Introduction, definition, text analysis reading, lecture listening test, and speaking discussion. Example. TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Bloom’s Taxonomy: higher-order thinking skills – LSU Centre for Academic Success
This short video provides a brief overview of Bloom’s taxonomy: classification of learning levels. It discusses each level but pays particular attention to the higher levels of analysing, evaluating and creating. It is a nice introduction to the theory of critical thinking. Example. Level: ***** [B2/C1] / Video [3.51] / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Critical Thinking: Bloom’s taxonomy cue questions
This information sheet provides a set of cue questions for each level of the taxonomy. A very helpful resource to accompany the theory of Bloom’s classification of thinking levels. TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
5 tips to improve critical thinking – Samantha Agoos
TED TALK: This lecture discusses briefly what is critical thinking and five key strategies to apply to improve critical thinking. It is a good listening as an introduction to criticality. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] / Video [4:16] TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Would you sacrifice one person to save five?– Eleanor Nelson
TED TALK: This lecture discusses an ethical dilemma called ‘The Trolley Problem’ devised by Philippa Foot (1967). It highlights why this type of ethical analysis is important in contemporary society. Example. Level: ***** [B1/B2/C1] / Video [4:35] / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Critical Thinking: questions to support critical reading
This information sheet provides a range of questions that should be applied when reading any academic text. The answers to these questions should be then applied in writing. TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Critical Thinking: cheat sheet infographic
This is a simple infographic offering questions that work to develop critical thinking on any given topic. Whenever your students discover or talk about new information, encourage them to use these questions for sparking debate and the sharing of opinions and insights among each other.TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Critical Thinking: a linear question sheet
This information sheet shows the development of an argument: from description to analysis and evaluation. It sets out a linear model of guiding questions that lead into each level of thinking (Plymouth University).TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*
Critical Thinking: Socratic questioning
This information sheet uses a range of socratic question under the topics of: clarifying, challenging, using evidence, exploring evidence, considering consequences and questioning the question (TES).TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
*